| |
Integrated module and gene-specific regulatory inference implicates upstream signaling networks |
| Sushmita Roy1,2, Stephen Lagree3, Zhonggang Hou4, James A. Thomson4,5, Ron M. Stewart4, Audrey P. Gasch 6 |
| |
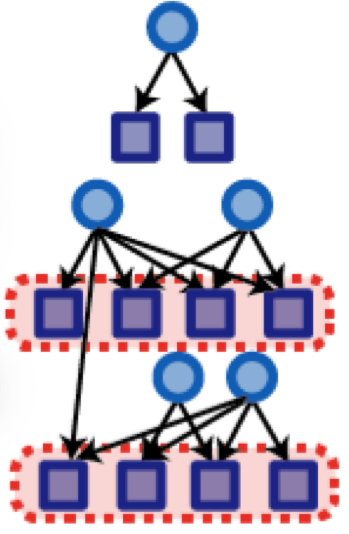 MERLIN is an algorithm for learning regulatory networks that strikes a balance between per-gene and per-module methods. MERLIN is an algorithm for learning regulatory networks that strikes a balance between per-gene and per-module methods.
Here you can download the software for applying MERLIN to different datasets.
|
| |
| |
| Abstract |
| |
| Regulatory networks that control gene expression are important in diverse biological contexts including stress re- sponse and development. Each gene’s regulatory program is determined by module-level regulation (e.g. co-regulation via the same signaling system) as well as gene-specific determinants that can fine-tune expression. We present a novel approach, Modular regulatory network learning with per gene information (MERLIN), that infers regulatory programs for individual genes while probabilistically constraining these programs to reveal module-level organization of regulatory networks. We use MERLIN to dissect global transcriptional behavior in two biological contexts: yeast stress response and human embryonic stem cell differentiation. Regulatory modules inferred by MERLIN capture co-regulatory re- lationships between signaling proteins and downstream transcription factors thereby revealing the upstream signaling systems controlling transcriptional responses. The inferred networks are enriched for regulators with genetic or physical interactions, supporting the inference, and identify modules of functionally related genes bound by the same transcrip- tional regulators. Our method combines the strengths of per-gene and per-module methods to reveal new insights into transcriptional regulation in stress and development. |
|
|
| |
| 1. Department of Biostatistics and Medical Informatics, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI 53715, USA |
| 2. Wisconsin Institute for Discovery, 330 N. Orchard Street, Madison, WI 53715, USA |
| 3. Department of Computer Science, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI 53715, USA |
| 4. Morgridge Institute for Research, 330 N. Orchard Street, Madison, WI 53715, USA |
| 5. Department of Cell and Regenerative Biology, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI 53715, USA |
| 6. Department of Genetics, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI 53715, USA |
|
|

